Introduction
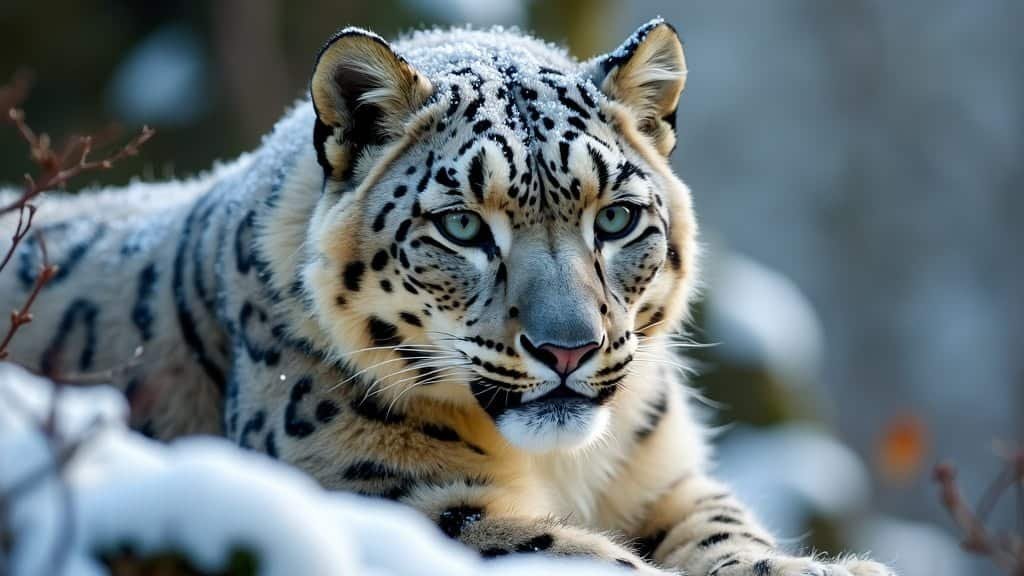
The snow leopard, known for its elusive nature and stunning beauty, possesses a coat pattern that is not only striking but also essential for its survival. This article explores how the snow leopard’s coat has evolved to provide camouflage in its harsh, mountainous environment
We will delve into the unique features of its fur, the benefits of camouflage in its natural habitat, the evolutionary factors at play, comparisons with other big cats, and the impact of climate change on its camouflage abilities
Understanding these aspects will give us a deeper appreciation of this magnificent creature’s adaptation to its surroundings
The Unique Features of Snow Leopard’s Coat Pattern
The snow leopard’s coat is one of its most distinguishing features, setting it apart from other big cats. Its smoky-gray fur, adorned with rosettes and spots, is perfectly suited to the rocky and snowy environments of its mountainous habitat
The snow leopard’s coat is not only beautiful but also an essential adaptation for survival, providing excellent camouflage that helps it remain undetected by both prey and predators
What Makes the Snow Leopard’s Coat Special?
The snow leopard’s coat has several unique features that contribute to its effectiveness as camouflage. The fur is dense and long, providing insulation against the cold temperatures of high-altitude environments
The coloration of the fur varies from smoky gray to a light tan, with a white underbelly. This coloration helps the snow leopard blend into the rocky and snowy landscapes it inhabits
One of the most striking features of the snow leopard’s coat is the rosettes and spots that cover its body. These patterns are not just randomly distributed; they are strategically placed to break up the outline of the animal’s body, making it less visible in its environment
The rosettes are larger and more irregularly shaped than those found on other big cats, such as leopards and jaguars, adding to the snow leopard’s unique appearance
The Role of Rosettes and Spots
The rosettes and spots on the snow leopard’s coat serve multiple purposes. Firstly, they provide effective camouflage by disrupting the outline of the animal’s body, making it harder for prey to detect it against the background of rocks and snow
The irregular shapes and sizes of the rosettes mimic the shadows and patterns found in the snow leopard’s natural habitat, enhancing its ability to remain concealed
Secondly, these patterns play a role in communication and identification. Each snow leopard has a unique pattern of rosettes and spots, much like a human fingerprint. This individuality helps snow leopards recognize each other and establish territories
The patterns can also indicate the health and fitness of the animal, as a healthy coat is often a sign of a well-nourished and well-adapted individual
Differences in Fur Color and Texture
The color and texture of the snow leopard’s fur can vary depending on its location and the time of year. In winter, the fur becomes thicker and lighter in color, providing better insulation and camouflage against the snow
In summer, the fur is shorter and can appear more yellowish or brownish, blending in with the rocky terrain. This seasonal variation in fur color and texture is another adaptation that helps the snow leopard survive in its changing environment
Moreover, the fur on the snow leopard’s belly is softer and denser than the fur on its back, providing extra warmth and protection when the animal is lying on cold surfaces
The long fur on the tail also serves multiple purposes: it provides balance when navigating steep and rocky terrain, and it can be wrapped around the body for additional warmth
Genetic Factors Influencing the Snow Leopard’s Coat Pattern
The unique coat pattern of the snow leopard is influenced by its genetic makeup. Researchers have identified specific genes responsible for the development of rosettes and spots in big cats. A study published in the journal Science in 2012 identified the gene Taqpep as a key regulator of coat pattern formation in felines
Mutations in this gene can lead to different patterns, such as stripes or spots, depending on the species. In snow leopards, variations in this gene result in the distinct rosettes and spots that provide effective camouflage
These genetic factors are subject to natural selection, with individuals possessing better camouflage having a higher chance of survival and reproduction. Over time, this has led to the evolution of the snow leopard’s coat pattern as an adaptation to its environment
Camouflage Benefits in the Snow Leopard’s Natural Habitat
Snow leopards inhabit some of the most rugged and remote mountain ranges in Central and South Asia, including the Himalayas, the Tien Shan, and the Altai Mountains. These regions are characterized by steep, rocky terrain and vast expanses of snow and ice
The snow leopard’s coat pattern is a crucial adaptation that allows it to blend seamlessly into this challenging environment, providing several key benefits that enhance its survival
Blending Into Rocky Terrains
One of the primary benefits of the snow leopard’s coat pattern is its ability to blend into rocky terrains. The rosettes and spots on the snow leopard’s fur mimic the shadows and textures of the rocks, making it difficult for prey to detect the predator as it moves stealthily through its habitat
This camouflage is particularly effective when the snow leopard is crouching or lying in wait for its prey, allowing it to get close enough to launch a surprise attack
The coloration of the fur also plays a vital role in this camouflage. The smoky-gray and light tan hues match the colors of the rocks and cliffs found in the snow leopard’s environment. This color match reduces the contrast between the animal and its surroundings, further enhancing its ability to remain undetected
The white underbelly, often visible only when the snow leopard is moving, helps it blend into the lighter, snowy areas of its habitat
Concealment in Snowy Environments
In addition to rocky terrains, snow leopards are also adept at blending into snowy environments. During the winter months, when the landscape is covered in snow, the lighter, denser fur of the snow leopard provides excellent camouflage
The white and gray tones of the fur match the snow, making it difficult for both prey and potential threats to spot the snow leopard from a distance
This ability to remain concealed in snowy environments is critical for the snow leopard’s hunting success. Snow leopards primarily prey on herbivores such as blue sheep (bharal), Himalayan tahr, and ibex, which are well-adapted to their mountain habitats and have keen senses to detect predators
The snow leopard’s camouflage allows it to approach these animals without being seen, increasing its chances of a successful hunt
Camouflage and Predator-Prey Dynamics
The snow leopard’s camouflage plays a significant role in the predator-prey dynamics of its ecosystem. By blending into its surroundings, the snow leopard can ambush its prey more effectively, reducing the amount of energy expended in chasing down animals over the rugged terrain
This efficiency is crucial in the harsh environments where food can be scarce, and the snow leopard needs to conserve energy to survive
Moreover, the snow leopard’s camouflage also helps it avoid detection by potential threats, such as humans and other large predators. Although the snow leopard is at the top of the food chain in its habitat, human activities such as poaching and habitat destruction pose significant risks
Effective camouflage helps the snow leopard remain hidden from hunters and other human disturbances, increasing its chances of survival
Scientific Studies on Snow Leopard Camouflage
Several scientific studies have examined the effectiveness of the snow leopard’s camouflage. A study published in the journal PLoS ONE in 2014 analyzed the coloration and patterning of snow leopard fur and its role in camouflage
The researchers found that the snow leopard’s coat pattern provides a high degree of concealment in both rocky and snowy environments, supporting the hypothesis that these patterns evolved as an adaptation to its habitat
Another study, conducted by the Snow Leopard Trust, used camera traps and remote sensing technology to study the behavior and habitat use of snow leopards. The findings revealed that snow leopards rely heavily on their camouflage to hunt and avoid detection, highlighting the importance of their coat pattern in their overall survival strategy
Evolutionary Factors Influencing the Snow Leopard’s Coat
The evolution of the snow leopard’s coat pattern is a fascinating process shaped by a combination of genetic, environmental, and adaptive factors
These factors have interacted over thousands of years to produce the distinctive and highly effective camouflage that characterizes the snow leopard today
Genetic Adaptations
The genetic basis for the snow leopard’s coat pattern lies in specific genes that regulate pigmentation and fur characteristics. One key gene is the Taqpep gene, which has been identified as a major regulator of pattern formation in felines
Mutations in this gene can result in different coat patterns, such as spots, stripes, or rosettes, depending on the species. In snow leopards, variations in the Taqpep gene contribute to the development of their unique rosettes and spots
A study published in the journal Science in 2012 explored the role of the Taqpep gene in various cat species, including the snow leopard. The researchers found that different mutations in this gene correspond to the distinct coat patterns seen in different feline species. For snow leopards, the specific mutations result in the large, irregular rosettes that provide such effective camouflage
In addition to the Taqpep gene, other genes involved in melanin production and fur growth also play a role in the snow leopard’s coat characteristics
The interaction of these genes determines the color, density, and pattern of the fur, which are crucial for the animal’s survival in its mountainous habitat
Environmental Pressures
The harsh and varied environments of the snow leopard’s habitat have exerted significant pressure on the evolution of its coat pattern
Snow leopards live in some of the highest and coldest mountain ranges in the world, where temperatures can drop well below freezing, and the landscape is often covered in snow and ice
In these conditions, having a coat that provides both insulation and camouflage is essential. The dense, long fur of the snow leopard offers excellent protection against the cold, while the coloration and patterning help it blend into the rocky and snowy environments. This dual function of the fur has been a critical factor in the snow leopard’s ability to survive and thrive in its habitat
Moreover, the snow leopard’s prey, such as blue sheep and ibex, are well-adapted to detect predators in their environment. This has created a selective pressure for snow leopards to develop more effective camouflage to approach their prey undetected
Over time, individuals with better-camouflaged coats would have had a higher success rate in hunting and thus a greater chance of passing on their genes
Evolutionary Timeline
The evolution of the snow leopard’s coat pattern can be traced back to its ancestral lineage. Snow leopards belong to the Panthera genus, which includes other big cats such as lions, tigers, leopards, and jaguars. The common ancestor of these big cats is believed to have lived around 6-10 million years ago
Through a process of speciation and adaptation to different environments, the various members of the Panthera genus developed distinct characteristics suited to their habitats
For snow leopards, the transition to high-altitude mountain ranges required adaptations for both cold weather and effective camouflage. The evolution of their coat pattern was a response to these environmental demands
Fossil evidence and genetic studies suggest that snow leopards diverged from other big cats around 2-4 million years ago. During this time, they adapted to the mountainous regions of Central and South Asia, developing the dense, rosette-patterned fur that is so effective for camouflage in rocky and snowy environments
Natural Selection and Adaptation
Natural selection has played a crucial role in shaping the snow leopard’s coat pattern. Individuals with better-camouflaged coats would have had a higher survival rate, as they could more effectively hunt prey and avoid detection by threats
These successful individuals would then pass on their advantageous traits to their offspring, gradually leading to the evolution of the species as a whole
Adaptation to the environment is an ongoing process, and snow leopards continue to face new challenges that may influence their coat pattern. For example, changes in climate and habitat due to human activities could affect the snow leopard’s environment, potentially leading to further adaptations in their camouflage strategies
Comparison with Other Big Cats’ Coat Patterns
Snow leopards share the Panthera genus with other big cats such as leopards, jaguars, tigers, and lions. While these species have evolved different coat patterns to suit their respective environments, there are interesting similarities and differences that highlight the unique adaptations of each
Differences with Leopards and Jaguars
Leopards and jaguars are the most similar to snow leopards in terms of having spotted coat patterns, but there are distinct differences in the size, shape, and distribution of these spots and rosettes
Leopards (Panthera pardus) have smaller, more closely spaced rosettes that are typically outlined with black and have a lighter center. This pattern is highly effective in the varied environments leopards inhabit, ranging from savannas to forests
Jaguars (Panthera onca), on the other hand, have larger rosettes with a more complex pattern that includes small spots within the rosettes. This dense, intricate pattern is well-suited for the dense, tropical rainforests of Central and South America, where jaguars are primarily found. The thicker and more complex pattern helps break up the jaguar’s outline among the dappled light of the forest
Snow leopards (Panthera uncia) have larger, more widely spaced rosettes and spots compared to leopards and jaguars
This pattern helps them blend into the rocky and snowy terrains of their high-altitude habitats. The snow leopard’s rosettes are more irregular in shape and less densely packed, which mimics the natural shadows and textures of their mountainous environment
Similarities with Other Mountain Cats
Other mountain-dwelling felines, such as the Eurasian lynx (Lynx lynx) and the clouded leopard (Neofelis nebulosa), also have coat patterns adapted to their environments. The Eurasian lynx has a spotted coat that provides camouflage in the forested and rocky areas of Europe and Asia
The clouded leopard, found in Southeast Asia, has a unique coat with large, cloud-shaped patterns that help it blend into the dense jungle foliage
Like the snow leopard, these mountain cats rely on their coat patterns for camouflage, hunting success, and survival. However, the specific adaptations of the snow leopard’s coat are unique to its high-altitude, cold, and rocky habitat
Unique Adaptations for Survival
The snow leopard’s coat is not only unique in its pattern but also in its structure and function. The fur is dense and long, providing essential insulation against the cold temperatures of its mountainous habitat
Unlike other big cats that live in warmer climates, the snow leopard’s fur has evolved to offer maximum protection from the harsh weather conditions of high altitudes
The snow leopard’s coat also features a unique blend of colors, ranging from smoky gray to light tan, with a white underbelly. This coloration helps the snow leopard blend into both rocky outcrops and snowy landscapes, offering versatile camouflage across its varied habitat
Furthermore, the snow leopard’s tail is thick and furry, unlike the tails of leopards and jaguars. This adaptation provides balance and agility when navigating steep and rugged terrains, and the tail can be wrapped around the body for additional warmth
Adaptation to Prey and Hunting Strategies
The snow leopard’s coat pattern also plays a crucial role in its hunting strategies. Unlike leopards and jaguars that hunt in more densely vegetated areas, snow leopards hunt in open, rocky, and snowy terrains. The large, irregular rosettes and spots break up the snow leopard’s outline, allowing it to stalk prey without being easily detected
Snow leopards primarily prey on mountain-dwelling herbivores such as blue sheep, Himalayan tahr, and ibex
These prey animals are highly vigilant and adapted to detecting predators in their environment. The snow leopard’s camouflage gives it the advantage of approaching these animals closely before launching a surprise attack
Impact of Climate Change on Snow Leopard’s Camouflage
Climate change poses significant challenges to the survival of many species, including the snow leopard
As temperatures rise and weather patterns shift, the snow leopard’s habitat and the effectiveness of its camouflage are both affected. Understanding these impacts is crucial for conservation efforts aimed at protecting this elusive big cat
Changes in Habitat
One of the most direct impacts of climate change on snow leopards is the alteration of their high-altitude habitats. Rising temperatures are causing glaciers to retreat and snow cover to diminish in many of the mountainous regions where snow leopards live
This reduction in snow cover affects the snow leopard’s camouflage, as their light-colored fur is adapted to blend into snowy environments. With less snow, the contrast between the snow leopard’s coat and its surroundings increases, making it easier for prey and potential threats to spot them
Additionally, climate change is causing shifts in vegetation and prey availability. As temperatures warm, plant species typically found at lower elevations may start to grow higher up in the mountains, altering the landscape
This can affect the distribution and abundance of the snow leopard’s prey, such as blue sheep and Himalayan tahr, which rely on specific types of vegetation. Changes in prey populations can force snow leopards to adapt their hunting strategies and potentially expand their range to find sufficient food
Effects on Coat Color and Pattern
While the genetic basis of the snow leopard’s coat color and pattern is relatively fixed, environmental factors can influence the expression of these traits
For instance, the density and thickness of the snow leopard’s fur can vary with seasonal changes, becoming thicker and lighter in winter and thinner and darker in summer. However, long-term shifts in climate can disrupt these patterns
If snow leopards experience consistently warmer temperatures, their fur may not adapt as effectively to seasonal changes, potentially reducing the effectiveness of their camouflage
For example, if winters become shorter and less snowy, the snow leopard’s winter coat may no longer provide optimal camouflage, leaving them more exposed. Similarly, prolonged exposure to higher temperatures can stress the animals, affecting their overall health and the condition of their fur
Future Adaptations
While snow leopards have shown remarkable adaptability over millions of years, the rapid pace of climate change presents unprecedented challenges. For snow leopards to continue thriving, they may need to develop new adaptations
These could include changes in behavior, such as altering hunting strategies or shifting their range to higher altitudes where temperatures remain cooler and snow cover persists
Conservation efforts can play a crucial role in supporting the snow leopard’s ability to adapt. Protecting and restoring high-altitude habitats, ensuring connectivity between different populations, and mitigating human-wildlife conflict are essential strategies. By maintaining healthy ecosystems and stable prey populations, conservationists can help snow leopards cope with the changing environment
Scientific Studies on Climate Change Impacts
Several studies have highlighted the potential impacts of climate change on snow leopards. A 2016 study published in Biological Conservation used climate models to predict future changes in the snow leopard’s habitat
The researchers found that up to 30% of the snow leopard’s current range could be lost due to rising temperatures and habitat degradation. This loss of habitat would further fragment snow leopard populations, making it more difficult for them to find mates and maintain genetic diversity
Another study, published in the journal Global Ecology and Conservation in 2019, examined the relationship between snow cover and snow leopard sightings. The study found that snow leopards were more frequently observed in areas with higher snow cover, suggesting that their camouflage is crucial for avoiding detection. As snow cover diminishes, snow leopards may become more vulnerable to poaching and human-wildlife conflict
Conservation Strategies
To mitigate the impacts of climate change on snow leopards, conservationists are employing a range of strategies
One key approach is creating and expanding protected areas that encompass a variety of altitudes and habitats, providing refuges where snow leopards can move in response to changing conditions. Transboundary conservation initiatives, such as those promoted by the Global Snow Leopard and Ecosystem Protection Program (GSLEP), aim to foster cooperation among countries that share snow leopard populations
Efforts to combat climate change at a global scale are also essential. Reducing greenhouse gas emissions, promoting sustainable land use practices, and supporting climate adaptation measures can help preserve the snow leopard’s habitat and the ecosystems they depend on
Conclusion
The snow leopard’s remarkable coat pattern is a testament to millions of years of evolution, allowing it to blend seamlessly into the harsh, rugged terrains of Central and South Asia
This intricate camouflage, characterized by large, irregular rosettes and spots, is crucial for its survival, aiding in both hunting and avoiding detection by threats. By examining the unique features of the snow leopard’s coat, the benefits of camouflage in its natural habitat, and the evolutionary factors at play, we gain a deeper appreciation for this elusive big cat
The comparison with other big cats highlights the unique adaptations that set the snow leopard apart, emphasizing its specialized evolution for mountainous environments
However, climate change presents new challenges, threatening the effectiveness of this camouflage and the very habitat it relies on. Conservation efforts, both localized and global, are essential to support the snow leopard’s continued survival and ability to adapt to a rapidly changing world
Understanding and protecting the snow leopard’s coat pattern and its role in camouflage is not only a scientific endeavor but also a crucial step in preserving one of the planet’s most majestic and mysterious creatures