Introduction
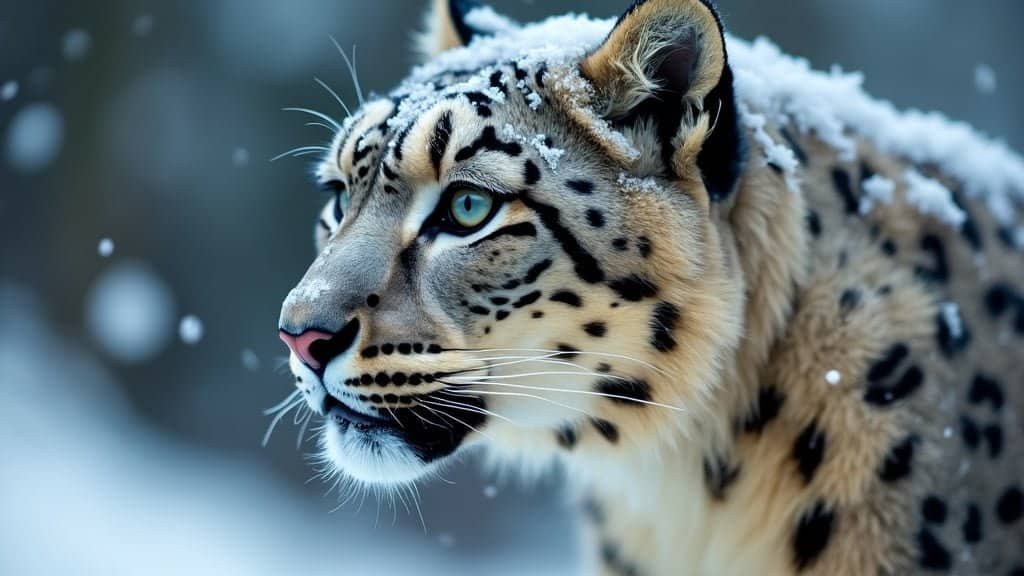
Snow leopards are renowned for their ability to thrive in the extreme high-altitude environments of Central Asia. This article explores the genetic adaptations that allow these magnificent cats to survive in such harsh conditions
We will delve into the specific genetic traits that enhance their respiratory and circulatory systems, the role of their thick fur, and the physical characteristics that aid their survival and hunting abilities. Additionally, we will examine how these adaptations help them maintain energy levels and regulate temperature in cold environments
Genetic Traits of Snow Leopards
Snow leopards possess a variety of unique genetic traits that enable them to thrive in the high-altitude regions of Central Asia
These adaptations are crucial for their survival in environments characterized by thin air, extreme cold, and rugged terrain. Understanding these genetic traits provides insight into how these magnificent creatures have evolved to become one of nature’s most efficient high-altitude predators
Key Genetic Markers
Research has identified specific genetic markers that contribute to the snow leopard’s ability to survive at high altitudes. One such marker is a variant of the EPAS1 gene, which plays a critical role in the body’s response to hypoxia, or low oxygen levels, common in high-altitude environments
This gene variant enhances the production of red blood cells, allowing snow leopards to maximize oxygen uptake and maintain their metabolic functions even in thin air
Adaptations in Fur and Skin
Snow leopards have adapted to their cold environments with a dense, woolly undercoat covered by longer, thick guard hairs. This fur provides excellent insulation against the cold, preventing heat loss and maintaining body temperature
Additionally, the fur on their belly is particularly thick, providing extra protection when they lie on cold surfaces. The skin underneath this fur also contains specialized cells that help in temperature regulation, ensuring that the snow leopard can remain active even in freezing temperatures
Skeletal and Muscular Adaptations
The skeletal and muscular structure of snow leopards is another area where genetic adaptations are evident. These big cats have powerful, compact limbs that allow them to navigate the steep, rocky terrains of their mountainous habitats with agility and precision
Their large paws act like snowshoes, distributing their weight more evenly and preventing them from sinking into the snow. Furthermore, strong hind limbs enable them to leap up to six times the length of their body, an essential trait for catching prey and moving across challenging landscapes
These genetic adaptations in their skeletal and muscular systems are complemented by their long, thick tails, which provide balance and stability when they are on the move. This combination of traits makes snow leopards exceptional climbers and hunters, perfectly suited for their high-altitude environments
Respiratory Adaptations
Snow leopards have developed remarkable respiratory adaptations that enable them to survive in the thin air of high-altitude environments. These adaptations are crucial for maintaining oxygen levels and ensuring their metabolic processes function efficiently in regions where oxygen is scarce
Enlarged Nasal Cavities
One of the most significant respiratory adaptations in snow leopards is their enlarged nasal cavities. These cavities are larger than those found in many other big cats, allowing for greater air intake with each breath
The increased surface area inside the nasal passages also helps to warm and humidify the cold, dry air before it reaches the lungs. This adaptation not only aids in maintaining body temperature but also ensures that the respiratory system functions optimally in frigid conditions
Efficient Oxygen Utilization
In addition to their enlarged nasal cavities, snow leopards have evolved to utilize oxygen more efficiently. Studies have shown that snow leopards possess a high concentration of hemoglobin in their blood
Hemoglobin is the protein responsible for carrying oxygen from the lungs to the rest of the body. The increased hemoglobin concentration allows for greater oxygen transport, ensuring that the muscles and organs receive an adequate supply even when atmospheric oxygen levels are low
Breathing Techniques in Thin Air
Snow leopards also employ specific breathing techniques that help them cope with the thin air at high altitudes. These techniques include deeper and slower breaths, which maximize the amount of oxygen taken in with each inhalation
Additionally, their respiratory rate adjusts dynamically based on activity levels and environmental conditions. For example, during periods of intense activity such as hunting or escaping predators, snow leopards can increase their breathing rate to boost oxygen intake
Adaptations in Lung Structure
The structure of snow leopards’ lungs is another critical adaptation. Their lungs are larger relative to their body size compared to other big cats, providing a greater capacity for air intake and oxygen exchange
The alveoli, small air sacs within the lungs where oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged, are more numerous and larger, enhancing the efficiency of gas exchange. This allows snow leopards to extract more oxygen from each breath, which is essential for sustaining their high-energy activities in oxygen-poor environments
These respiratory adaptations are vital for snow leopards’ survival, allowing them to maintain their physical capabilities and metabolic functions even in the challenging conditions of their high-altitude habitats. By optimizing their respiratory system, snow leopards can thrive in environments that would be inhospitable to many other species
Role of Fur in Survival
The thick fur of snow leopards is one of their most crucial adaptations for survival in high-altitude environments. This fur is not just for insulation; it serves multiple functions that help these cats endure the harsh conditions of their mountainous habitats
Insulating Properties
The primary role of the snow leopard’s fur is to provide insulation against the extreme cold. Snow leopards have a dense undercoat made of short, fine hairs that trap heat close to the body, and longer, coarser guard hairs that form a protective layer on top
This dual-layer fur system is highly effective at retaining body heat, even in temperatures that can drop as low as -40°F. The thick fur also covers their large paws, which not only helps in insulation but also acts as natural snowshoes to distribute their weight when walking on snow
Seasonal Fur Changes
Snow leopards undergo seasonal changes in their fur to adapt to varying temperatures throughout the year. In the winter, their fur becomes thicker and denser, providing maximum insulation during the coldest months
As the weather warms up in the summer, they shed some of this fur to prevent overheating. This ability to adjust their fur density helps snow leopards maintain a stable body temperature year-round, regardless of the external temperature fluctuations
Protection Against the Elements
The fur of snow leopards also offers protection against other environmental elements. The long guard hairs are slightly oily, making them water-resistant and helping to keep the undercoat dry in wet conditions
This is particularly important during heavy snowfalls or when the snow leopards are exposed to melting snow. Additionally, the fur provides a degree of protection against the harsh wind that is common in their mountainous habitats, reducing the impact of wind chill on their bodies
Camouflage
The coloration and pattern of snow leopards’ fur play a critical role in their survival by providing camouflage. Their fur is marked with rosettes and spots that blend seamlessly with the rocky, snowy landscapes they inhabit
This natural camouflage helps them remain undetected by both prey and predators, enhancing their ability to hunt and avoid danger. The ability to blend into their surroundings is particularly important for snow leopards, as it allows them to approach prey more closely and conserve energy during hunting
Fur Density and Length
The density and length of snow leopards’ fur are specifically adapted to their high-altitude environments. Their fur can be up to 5 inches long on the back and sides, providing extensive coverage and insulation
This long fur is especially important during periods of rest, when snow leopards lie down on cold surfaces. The thick fur on their belly and chest ensures that they do not lose too much body heat to the ground
These various aspects of their fur enable snow leopards to survive and thrive in some of the harshest environments on Earth. The insulating properties, seasonal changes, protective features, and camouflage all contribute to their ability to maintain body temperature, avoid detection, and protect against the elements
Physical Characteristics
Snow leopards possess unique physical characteristics that are essential for their survival in high-altitude environments. These features enhance their mobility, hunting efficiency, and overall ability to thrive in rugged, mountainous terrains
Strong Limbs and Paws
Snow leopards have exceptionally strong limbs, which are critical for navigating the steep, rocky landscapes of their habitats. Their powerful legs enable them to leap as far as 50 feet in a single bound, allowing them to traverse large gaps between rocks and cliffs effortlessly
The musculature in their limbs is well-developed, providing the strength needed for climbing and jumping. Additionally, their large paws distribute their weight evenly, acting like natural snowshoes that prevent them from sinking into deep snow and helping them maintain balance on slippery surfaces
Tail Functionality
The long, thick tail of a snow leopard is another key physical adaptation. Measuring up to 3 feet in length, the tail serves multiple functions. It acts as a counterbalance when leaping and climbing, enhancing their agility and stability
The tail is also covered in dense fur, providing additional warmth when wrapped around their body during rest periods. This dual-purpose tail is essential for maintaining both balance and body temperature in their cold, mountainous environment
Camouflage in the Snow
The snow leopard’s fur is not only thick and insulating but also patterned with rosettes and spots that provide excellent camouflage. This coloration helps them blend into the rocky and snowy landscapes, making it easier to approach prey undetected and avoid potential predators
The ability to remain concealed in their environment is crucial for their hunting strategy, which often involves stalking and ambushing prey
Skeletal Structure
The skeletal structure of snow leopards is specially adapted to their high-altitude habitats. They have a robust, flexible spine that allows for agile movements and swift changes in direction. This flexibility is particularly useful when chasing prey across uneven terrain
Their relatively short forelimbs and longer hind limbs give them a distinctive gait that is efficient for climbing and jumping. These skeletal adaptations contribute to their exceptional ability to maneuver through their rugged environment with ease
Vision and Hearing
Snow leopards have keen vision and hearing, which are vital for detecting prey and navigating their environment. Their eyes are adapted to low-light conditions, allowing them to hunt during dawn, dusk, and nighttime
The reflective layer behind their retina, known as the tapetum lucidum, enhances their night vision by reflecting light back through the retina, improving their ability to see in dim conditions. Additionally, their acute hearing helps them detect the faint sounds of prey moving in the snow or hiding among rocks
Dietary Adaptations
The dietary habits of snow leopards are also influenced by their physical characteristics. They are carnivorous and primarily hunt wild sheep and goats, but they are also opportunistic feeders, preying on smaller mammals and birds when necessary
Their powerful jaws and sharp teeth are well-suited for gripping and tearing flesh, enabling them to efficiently consume their prey. Snow leopards have a relatively low metabolic rate compared to other big cats, which helps them conserve energy in their resource-scarce environments
These physical characteristics collectively enable snow leopards to excel in their high-altitude habitats. Their strong limbs, functional tail, effective camouflage, robust skeletal structure, and keen senses all contribute to their ability to hunt, navigate, and survive in some of the most challenging environments on the planet
Hunting Abilities
Snow leopards have evolved a suite of hunting abilities that allow them to thrive in their high-altitude environments. These abilities are critical for securing food in a habitat where prey can be scarce and difficult to catch
Stealth and Speed
One of the primary hunting strategies of snow leopards is their ability to approach prey with exceptional stealth. Their camouflaged fur allows them to blend into the rocky and snowy landscapes, making it easier to get close to their prey without being detected
They typically hunt during dawn and dusk when visibility is low, further aiding their stealth. Once close enough, snow leopards rely on short bursts of speed to chase down and capture their prey. They can sprint quickly over short distances, using their powerful hind legs to propel them forward with great force
Prey Detection and Capture
Snow leopards have keen senses that help them detect prey from a distance. Their excellent vision allows them to spot movement from afar, and their acute hearing can pick up the sounds of animals moving in the snow or among rocks
When a potential prey is identified, snow leopards employ a combination of stalking and ambushing techniques. They often use the terrain to their advantage, approaching from above or behind cover to remain unseen until the last moment. Their strong limbs and sharp claws are essential for gripping and subduing prey once they make contact
Energy Conservation Strategies
Hunting in high-altitude environments requires significant energy, and snow leopards have developed strategies to conserve energy during the process. They are known for their patience, often spending hours or even days tracking and stalking a single animal
This careful approach minimizes unnecessary exertion and increases the likelihood of a successful hunt. Snow leopards also take advantage of the terrain, using gravity to assist in their downward chases and avoiding long, energy-draining pursuits
Hunting Techniques
Snow leopards use various hunting techniques tailored to their environment and the type of prey. For larger prey such as wild sheep and goats, they often employ a powerful pounce to knock the animal off balance or off a cliff
This method relies on their strength and agility to deliver a quick, fatal blow. For smaller prey, they might use a combination of stalking and rapid pursuit to catch the animal by surprise. Their flexible spine and strong, muscular build allow them to make sudden, agile movements that are critical in close-range chases
Diet and Prey Preferences
Snow leopards are carnivorous and have a diet primarily consisting of wild sheep and goats, such as the bharal (blue sheep) and the ibex. They also hunt smaller mammals, birds, and occasionally scavenge if necessary
The availability of prey can vary seasonally, influencing their hunting patterns and diet. During the winter months, when prey animals are less mobile and easier to catch, snow leopards might hunt more frequently
Conversely, in the summer, when prey animals are more dispersed and agile, snow leopards may rely more on smaller mammals and birds
Adaptations for High-Altitude Hunting
High-altitude hunting presents unique challenges, and snow leopards have several adaptations that make them effective hunters in these environments. Their large nasal passages enhance oxygen intake, which is crucial during the physical exertion of hunting
Their powerful muscles and robust cardiovascular system support sustained activity in low-oxygen conditions. Additionally, their thick fur not only provides insulation but also offers protection from the sharp rocks and rough terrain they encounter during hunts
The combination of stealth, speed, acute senses, and specialized hunting techniques makes snow leopards formidable predators in their high-altitude habitats. These abilities ensure they can secure enough food to survive and reproduce, maintaining their position as apex predators in some of the harshest environments on Earth
Conclusion
Snow leopards are extraordinary creatures uniquely adapted to survive in the harsh conditions of high-altitude environments
Their genetic traits, such as specific gene variants and physical adaptations, enhance their respiratory efficiency and overall ability to thrive where oxygen is scarce. The dense, multi-layered fur of snow leopards provides essential insulation against extreme cold, while their robust skeletal and muscular structures allow for agile movement across rugged terrains
Their powerful limbs and large paws aid in navigating the snowy, rocky landscapes, and their long tails provide balance and warmth. Snow leopards’ keen vision and hearing, combined with their natural camouflage, make them formidable hunters capable of stealthily approaching and capturing prey
They have developed specialized hunting techniques that optimize energy conservation and increase the likelihood of successful hunts in environments where prey is not always abundant
Overall, the genetic and physical adaptations of snow leopards highlight their incredible ability to endure and flourish in some of the most challenging habitats on Earth. By understanding these adaptations, we gain deeper insight into the evolutionary processes that shape the survival strategies of high-altitude wildlife