Introduction
Natural selection plays a crucial role in shaping the evolution of snow leopards, leading to their unique adaptations for survival in some of the world’s harshest environments
This article explores how natural selection has influenced their physical traits, the impact of their environment on their evolution, the genetic changes they’ve undergone, their hunting strategies, and the challenges they face that drive their ongoing evolution
Through this detailed examination, we gain a deeper understanding of how snow leopards have become the remarkable predators they are today and what the future might hold for them in the face of changing environmental pressures
Influence of Natural Selection on Physical Traits
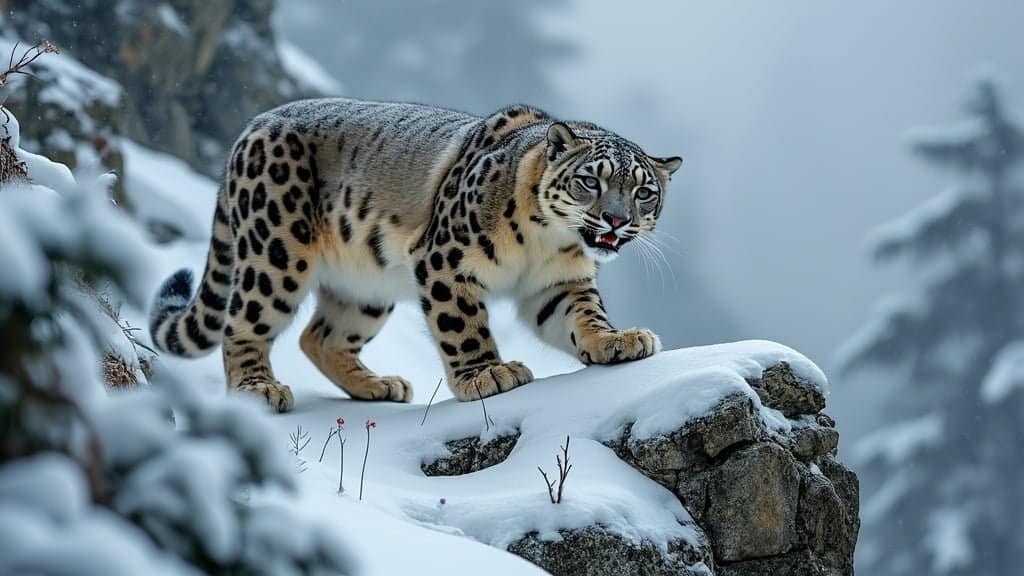
Natural selection has significantly shaped the physical traits of snow leopards, enabling them to thrive in the challenging environments of the high mountains of Central Asia. These adaptations have emerged over thousands of years, allowing snow leopards to become efficient hunters and survivors in their harsh habitat
Adaptations for Cold Climate
Snow leopards have developed several key adaptations to cope with the extreme cold of their mountainous environments
Their thick, dense fur provides excellent insulation against the cold. This fur is not only long and warm but also has a unique pattern of rosettes and spots that help with camouflage in the rocky, snowy terrain
Another crucial adaptation is their large nasal cavities, which warm the cold air before it reaches their lungs. This physiological trait is essential for surviving at high altitudes, where temperatures can plummet drastically. Additionally, their short, rounded ears minimize heat loss, further aiding in thermoregulation
Evolution of Fur and Skin
The fur and skin of snow leopards have evolved to serve multiple functions. The outer fur is long and water-resistant, protecting the snow leopard from wet snow and icy conditions. Underneath this outer layer is a dense undercoat that provides insulation by trapping air and retaining body heat
The coloration of their fur, a blend of whites, grays, and browns, not only aids in camouflage but also helps to regulate body temperature. The spots and rosettes on their fur break up their outline against the rocky background, making it easier for them to stalk prey undetected
Skeletal and Muscular Adaptations
Snow leopards possess several skeletal and muscular adaptations that enhance their ability to navigate and hunt in rugged terrains
Their limbs are short but powerful, providing the strength needed to climb steep slopes and leap across rocks. Their large paws act like natural snowshoes, distributing their weight evenly and allowing them to walk on snow without sinking
The tail of a snow leopard is another remarkable adaptation. Long and thick, it aids in balance when navigating precarious cliffs and serves as a wrap-around blanket to protect their face and vital organs from the cold when resting
The combination of these adaptations highlights how natural selection has honed the physical traits of snow leopards to ensure their survival and success as apex predators in some of the most inhospitable regions on Earth
Environmental Impact on Evolution
The harsh and varied environments in which snow leopards live have played a pivotal role in their evolution. Natural selection has driven the development of traits that enable these big cats to survive and thrive in some of the most challenging terrains on the planet
Habitat and Terrain Challenges
Snow leopards inhabit the mountainous regions of Central and South Asia, including the Himalayas, the Tibetan Plateau, and the Altai Mountains
These areas are characterized by steep, rocky slopes, deep snow, and extreme altitudes, often exceeding 18,000 feet. The terrain presents significant challenges, requiring snow leopards to be highly agile and capable of making impressive leaps across vast distances
The rugged landscape has influenced the evolution of snow leopards’ physical abilities
Their powerful hind legs enable them to jump up to 50 feet in a single bound, an adaptation essential for navigating cliffs and chasing prey across broken ground. The ability to blend into the rocky environment is another critical adaptation, allowing them to remain undetected by both prey and potential threats
Role of Altitude and Temperature
The high-altitude habitats of snow leopards come with low oxygen levels and extremely cold temperatures
Natural selection has favored individuals with adaptations that allow them to cope with these conditions. Their large chest cavities and robust lungs enable them to breathe efficiently in thin air, while their thick fur and dense undercoat provide insulation against the freezing temperatures
These adaptations are not just physical; snow leopards have also developed behavioral strategies to cope with their environment. They are primarily crepuscular, meaning they are most active during dawn and dusk when temperatures are slightly warmer. This behavior helps them conserve energy and avoid the coldest parts of the day
Impact of Prey Availability
The availability of prey in the mountainous regions has also driven the evolution of snow leopards. Their primary prey includes blue sheep, ibex, and other mountain ungulates, which are also adapted to the high-altitude environment
The scarcity and unpredictability of prey have made snow leopards opportunistic hunters, capable of taking down a variety of animals, from small rodents to large mammals
Natural selection has favored traits that enhance hunting efficiency, such as exceptional stealth and powerful limbs for quick, decisive attacks. Snow leopards’ keen eyesight and acute hearing further aid in detecting prey in the vast, open landscapes
The environmental pressures of high altitudes, cold temperatures, and scarce prey have collectively shaped the evolution of snow leopards, ensuring they possess the necessary physical and behavioral adaptations to survive and thrive in their unique habitats
Genetic Changes Due to Natural Selection
Genetic adaptations play a crucial role in the evolution of snow leopards, enabling them to thrive in their challenging environments. Through natural selection, snow leopards have developed genetic traits that support their survival and reproduction in high-altitude, cold, and rugged terrains
Genetic Mutations and Variations
Genetic mutations and variations are fundamental to the process of natural selection. In snow leopards, these mutations have led to advantageous traits being passed down through generations. For instance, specific genes related to fur density, coloration, and growth patterns have evolved to provide better insulation and camouflage in snowy environments
One significant genetic adaptation is the mutation in the EGLN1 gene, which affects the body’s response to low oxygen levels at high altitudes
This mutation allows snow leopards to thrive in environments with low oxygen availability by enhancing their blood’s ability to carry oxygen more efficiently. Studies have shown that similar mutations are present in other high-altitude animals, such as Tibetan antelopes and yaks
Hereditary Traits and Adaptations
Several hereditary traits have emerged in snow leopards due to natural selection. These traits include their robust cardiovascular systems, which support their ability to endure physical exertion in thin air
Additionally, genetic adaptations affecting muscle fiber composition contribute to their strength and agility, essential for navigating steep and rocky terrains
Snow leopards also possess unique genetic adaptations related to their sensory systems. Enhanced olfactory and auditory genes allow them to detect prey and predators from a distance, providing a critical survival advantage in their expansive habitats
Studies on Snow Leopard Genetics
Recent genetic studies have provided valuable insights into the evolutionary history of snow leopards
For example, a genomic analysis conducted by scientists from the Chinese Academy of Sciences revealed that snow leopards diverged from other big cats around 4 million years ago . This divergence was likely driven by their adaptation to high-altitude environments
Further research has identified several genes associated with cold tolerance, such as those involved in lipid metabolism, which help snow leopards maintain energy levels in freezing temperatures. These genetic adaptations are crucial for their survival, as they enable snow leopards to hunt and reproduce effectively in harsh conditions
Understanding the genetic changes due to natural selection helps us appreciate the intricate mechanisms behind the evolution of snow leopards. These genetic traits are not only a testament to the power of natural selection but also highlight the resilience and adaptability of this remarkable species
Hunting Strategies and Survival Mechanisms
The survival of snow leopards in their harsh environments is a testament to their highly specialized hunting strategies and survival mechanisms
Natural selection has played a critical role in honing these abilities, ensuring that snow leopards remain effective apex predators in their mountainous habitats
Stealth and Camouflage
Snow leopards have evolved to be masters of stealth and camouflage, which are vital for their hunting success
Their fur, with its unique pattern of rosettes and spots, provides excellent camouflage against the rocky and snowy terrain. This natural disguise allows them to approach their prey undetected, increasing their chances of a successful hunt
Their ability to move silently is another critical adaptation. Snow leopards possess soft footpads that enable them to tread quietly over rocky ground and snow. This silent movement is crucial for stalking prey, as any noise could alert their target and cause it to flee
Hunting Techniques and Success Rates
Snow leopards employ a variety of hunting techniques tailored to their environment and the type of prey they pursue. They primarily hunt mountain ungulates such as blue sheep, ibex, and Himalayan tahr, but they are also known to take smaller mammals and birds when larger prey is scarce
One of their primary hunting strategies involves ambushing prey from above. Snow leopards use the rugged terrain to their advantage, leaping down onto their prey from elevated positions. This tactic minimizes the distance between them and their target, reducing the chance of escape
Another technique is the chase. While snow leopards are not known for their endurance, they can make short, explosive sprints to catch prey. Their powerful hind legs allow them to leap great distances, sometimes covering over 30 feet in a single bound. This ability is particularly useful in the steep, uneven terrain where their prey often tries to escape
Studies on hunting success rates indicate that snow leopards are successful in approximately 30-50% of their hunts, a relatively high success rate compared to other big cats. This efficiency is a direct result of their specialized hunting skills and adaptations honed by natural selection
Adaptations for Prey Capture
Several physical and behavioral adaptations have evolved in snow leopards to enhance their ability to capture and subdue prey
Their sharp, retractable claws provide a strong grip on slippery and uneven surfaces, as well as on their prey during the capture. Their large, powerful jaws and sharp teeth are adapted to delivering lethal bites to the neck or throat of their prey, ensuring a quick kill
Snow leopards also exhibit remarkable strength and agility, allowing them to wrestle with prey that can often be larger and heavier than themselves. This physical prowess is complemented by their patience and perseverance. Snow leopards are known to wait for hours, sometimes even days, for the perfect moment to strike, showcasing their incredible dedication to securing a meal
Natural selection has fine-tuned these hunting strategies and survival mechanisms over millennia, enabling snow leopards to remain at the top of the food chain in their challenging environments. These adaptations not only ensure their survival but also highlight the intricate and dynamic relationship between predator and prey in the wild
Challenges and Future Evolution
Snow leopards face numerous challenges that impact their survival and drive their continued evolution. Understanding these challenges is crucial for conservation efforts and predicting potential future adaptations
Current Threats and Natural Selection
Several current threats pose significant challenges to snow leopards, influencing the natural selection process
Habitat loss due to human activities, such as mining, infrastructure development, and livestock grazing, reduces the available territory for snow leopards to hunt and breed. This fragmentation of habitat can lead to isolated populations, reducing genetic diversity and increasing the risk of inbreeding
Another critical threat is poaching. Snow leopards are hunted for their beautiful fur and bones, which are used in traditional medicine. Despite international protection, illegal hunting remains a serious issue
Poaching not only directly reduces snow leopard populations but also disrupts the natural selection process by removing strong, healthy individuals from the gene pool
Human-wildlife conflict also poses a significant threat. As snow leopards prey on livestock, herders sometimes retaliate by killing them. This conflict can lead to a decline in snow leopard numbers and may force the species to adapt their hunting behavior to avoid humans, potentially impacting their natural hunting strategies
Potential Future Adaptations
Given the rapid environmental changes and ongoing threats, snow leopards may undergo several future adaptations. These adaptations could be driven by the need to survive in altered habitats, cope with new challenges, and exploit available resources more efficiently
One potential adaptation could be changes in diet and hunting behavior. As traditional prey species decline due to habitat loss and climate change, snow leopards may increasingly prey on smaller mammals and birds. This shift could lead to evolutionary changes in their physical traits, such as smaller size and altered hunting techniques to capture smaller prey more effectively
Another possible future adaptation is increased tolerance to human presence. As human activities encroach further into snow leopard habitats, individuals that can coexist with humans without conflict may have a survival advantage
This adaptation could involve behavioral changes, such as avoiding human settlements or becoming more nocturnal to minimize encounters with humans
Conservation Efforts and Evolution
Conservation efforts play a crucial role in shaping the future evolution of snow leopards. By mitigating threats and protecting habitats, conservationists can support the natural selection processes that enable snow leopards to adapt to their changing environments
Key conservation strategies include establishing and expanding protected areas, promoting sustainable land use practices, and engaging local communities in conservation efforts. By reducing habitat fragmentation and human-wildlife conflict, these measures can help maintain genetic diversity and support healthy snow leopard populations
Additionally, research and monitoring programs are essential for understanding the genetic and ecological needs of snow leopards. By studying their behavior, genetics, and interactions with the environment, scientists can identify critical factors influencing their evolution and develop targeted conservation strategies
Conclusion
Snow leopards are a testament to the power of natural selection, evolving unique adaptations to thrive in some of the most challenging environments on Earth
This article has explored how natural selection has influenced their physical traits, the impact of their environment on their evolution, the genetic changes they’ve undergone, their hunting strategies, and the challenges they face that drive their ongoing evolution. Each aspect highlights the intricate relationship between snow leopards and their habitat, emphasizing the delicate balance necessary for their survival
As we look to the future, it is clear that continued conservation efforts are essential to support the ongoing evolution and survival of this remarkable species
By protecting their habitats, mitigating human-wildlife conflicts, and addressing the threats of poaching and climate change, we can help ensure that snow leopards continue to thrive for generations to come. The story of the snow leopard is one of resilience and adaptation, a powerful reminder of the natural world’s ability to evolve in response to its ever-changing challenges