Introduction
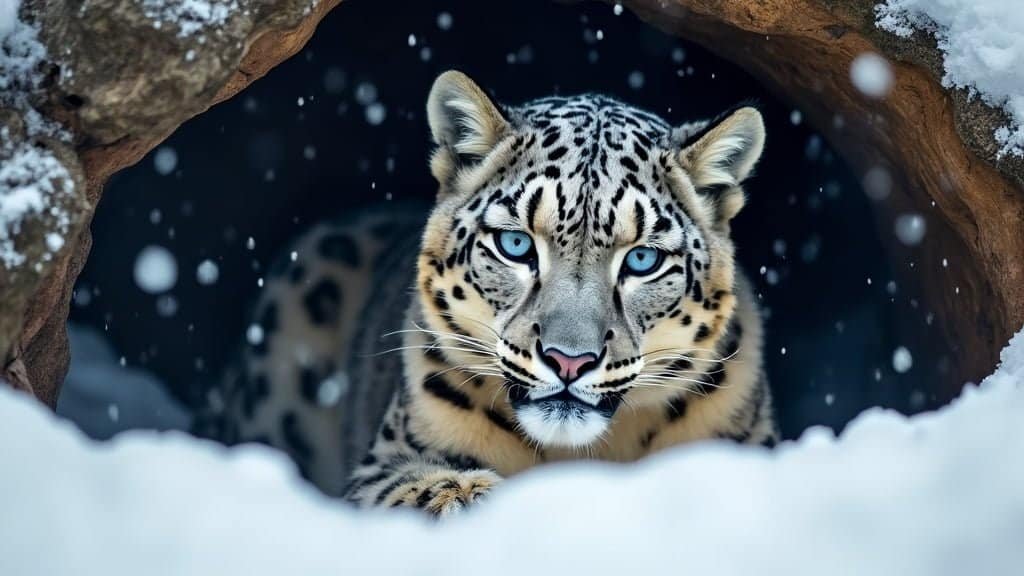
Snow leopards are renowned for their ability to thrive in some of the harshest climates on Earth. From the snowy peaks of the Himalayas to the rocky terrains of Central Asia, these elusive big cats exhibit remarkable adaptations that allow them to survive and prosper in diverse environments
In this article, we will explore the physical, behavioral, and genetic adaptations that enable snow leopards to navigate different climatic conditions. Additionally, we will discuss how climate change impacts these adaptations and what this means for the future of snow leopards
Physical Adaptations of Snow Leopards
Snow leopards are highly adapted to survive in the cold, rugged terrains they inhabit. Their physical characteristics have evolved to meet the challenges of their environment, ensuring they can hunt, move, and stay warm in extreme conditions
Thick Fur and Seasonal Changes
One of the most noticeable adaptations of snow leopards is their thick, dense fur, which provides insulation against the cold. Their fur is composed of two layers: a dense undercoat that keeps them warm and an outer layer of longer, coarse hair that protects against wind and moisture
This dual-layered fur is essential for survival in the freezing temperatures of the high-altitude regions they inhabit. During winter, their fur becomes even thicker and longer, enhancing their insulation
Studies have shown that the fur of snow leopards has a unique pattern of spots and rosettes that provides camouflage in their rocky, snowy habitats, helping them blend into the landscape and avoid detection by prey and predators
Large Paws for Snowy Terrains
Snow leopards have large, wide paws that act like natural snowshoes, distributing their weight more evenly and preventing them from sinking into the snow. This adaptation is crucial for navigating the deep snow of their mountainous habitats. Their paws are also covered in fur, which provides additional insulation and protection against the cold and rough surfaces they often encounter
Research indicates that the wide, fur-covered paws of snow leopards help them move efficiently and quietly through their environment, which is essential for hunting prey such as blue sheep and ibex that are well-adapted to the same rugged terrains
Strong Muscular Build
The muscular build of snow leopards is another key adaptation that supports their survival in harsh conditions. Their powerful legs allow them to leap great distances, which is necessary for navigating the rocky cliffs and steep slopes of their habitats. Snow leopards can leap up to 50 feet in a single bound, enabling them to catch prey and escape potential threats
Their long, thick tail provides balance and stability, acting as a counterbalance when they are moving across precarious terrain. Additionally, the tail serves as a blanket, which the snow leopard wraps around its body to stay warm while resting
Behavioral Adaptations to Climatic Conditions
Snow leopards exhibit a range of behavioral adaptations that enable them to cope with the varying climatic conditions of their habitats. These behaviors are crucial for their survival, ensuring they can hunt efficiently, conserve energy, and find shelter in extreme environments
Hunting Techniques in Various Climates
Snow leopards have developed specific hunting techniques that vary according to the climatic conditions and terrain. In snowy regions, they use their camouflage to blend into the surroundings and stalk their prey undetected
They rely on their agility and strength to ambush prey, often leaping from high vantage points. In rocky terrains, they use the natural cover provided by the landscape to approach their prey stealthily
Research indicates that snow leopards are opportunistic hunters, capable of adapting their hunting strategies based on the availability of prey and environmental conditions. For example, in areas where larger prey is scarce, they may hunt smaller mammals and birds to sustain themselves
Shelter and Denning Habits
Finding shelter is essential for snow leopards, especially in extreme weather conditions. They typically seek out caves, crevices, and rocky outcrops to create dens that offer protection from the elements. These dens are often located in remote, hard-to-reach areas, providing safety from potential predators and human disturbances
Snow leopards use their dens for resting, raising cubs, and sheltering from harsh weather. During the breeding season, females give birth in these secluded locations, ensuring their cubs are born in a secure environment. Studies have shown that denning sites are chosen based on factors such as elevation, slope, and proximity to prey-rich areas
Energy Conservation Strategies
Surviving in harsh climates requires efficient energy management. Snow leopards exhibit several behaviors that help them conserve energy. During periods of extreme cold or food scarcity, they may reduce their activity levels to minimize energy expenditure. They are also known to cache surplus food, which they can return to during lean times
Research has highlighted that snow leopards often adjust their activity patterns based on the season and availability of prey. For instance, they may become more nocturnal in areas with high human activity to avoid disturbances and increase their hunting success
Dietary Adaptations Across Habitats
Snow leopards’ diets are highly adaptable, allowing them to thrive in diverse environments where prey availability can vary significantly. Understanding these dietary adaptations provides insight into how snow leopards maintain their nutritional needs across different habitats
Prey Availability in Different Regions
Snow leopards primarily hunt large ungulates, such as blue sheep (bharal), ibex, and argali, which are abundant in their mountainous habitats
In regions where these larger prey animals are less common, snow leopards adapt by hunting smaller mammals like marmots, pikas, and hares. This flexibility in diet is crucial for their survival, especially in areas where prey populations fluctuate seasonally
Studies indicate that snow leopards may travel significant distances to find food, which is essential in regions with sparse prey availability. This ability to roam across large territories helps them locate and exploit different prey resources throughout the year
Seasonal Diet Changes
Seasonal variations significantly impact the diet of snow leopards. During the summer months, when prey animals such as blue sheep and ibex move to higher altitudes to graze, snow leopards follow them, adapting their hunting strategies to the new terrain and conditions. In the winter, when these prey animals descend to lower altitudes, snow leopards adjust their hunting patterns accordingly
Research shows that snow leopards also take advantage of carrion, particularly during harsh winter months when hunting conditions are more challenging, and prey is scarcer. This opportunistic feeding behavior helps them conserve energy and sustain themselves when live prey is difficult to catch
Impact of Habitat on Feeding Behavior
The habitat in which a snow leopard lives directly influences its feeding behavior. In rocky and rugged terrains, snow leopards use the landscape to their advantage, employing ambush tactics to catch their prey. In more open areas, they rely on stealth and speed to approach and capture animals
Additionally, snow leopards in different regions have been observed to hunt a variety of prey species based on local availability. For example, in some parts of the Himalayas, they have been known to prey on livestock, which can lead to human-wildlife conflicts. Conservation efforts aim to mitigate these conflicts by promoting practices such as livestock insurance and improved herding techniques
Genetic Adaptations to Diverse Climates
Snow leopards have evolved various genetic adaptations that enable them to survive and thrive in the diverse and often harsh climates across their range. These genetic traits help them cope with extreme temperatures, high altitudes, and varying prey availability
Genetic Variations Across Populations
Genetic studies have revealed significant variations among snow leopard populations across their range, which spans from the Himalayas to Central Asia. These variations are indicative of the different environmental pressures faced by snow leopards in different regions
For instance, snow leopards living in higher altitudes have developed genetic traits that help them utilize oxygen more efficiently, crucial for survival in low-oxygen environments
Research conducted by the Snow Leopard Trust and other conservation organizations has shown that these genetic differences are vital for the adaptability and resilience of snow leopards. Conservation efforts must consider these genetic variations to ensure the protection of diverse snow leopard populations
Adaptations to Cold Environments
One of the key genetic adaptations in snow leopards is their ability to thrive in cold environments. Their genes have evolved to support the production of dense, insulating fur, and a robust metabolic system that generates and conserves body heat efficiently
Additionally, snow leopards possess a unique form of hemoglobin that enhances their ability to transport oxygen in their blood, which is particularly beneficial at high altitudes where oxygen levels are low
A study published in the journal Science highlighted that the EPAS1 gene, which is involved in the body’s response to hypoxia (low oxygen levels), is significantly different in snow leopards compared to other big cats. This genetic adaptation is a crucial factor in their ability to live and hunt at high elevations
Genetic Research and Findings
Ongoing genetic research continues to uncover new insights into the adaptations of snow leopards
Advanced techniques such as genome sequencing have allowed scientists to identify specific genes associated with cold tolerance, efficient metabolism, and other survival traits. These findings are not only fascinating from a scientific perspective but also critical for conservation planning
For instance, genetic studies have been instrumental in understanding the connectivity between different snow leopard populations. By analyzing genetic markers, researchers can assess the genetic diversity within and between populations, which is essential for maintaining healthy and resilient snow leopard populations
Impact of Climate Change on Snow Leopard Adaptations
Climate change poses significant challenges to snow leopards, potentially affecting their habitats, prey availability, and the adaptations that have enabled their survival in harsh environments. Understanding these impacts is crucial for developing effective conservation strategies
Changes in Habitat Due to Climate Change
Climate change is causing significant alterations in the habitats of snow leopards. Rising temperatures and shifting weather patterns are leading to the melting of glaciers and reduced snow cover in mountainous regions. These changes can force snow leopards to move to higher altitudes in search of suitable habitat, which may not always be available
Research indicates that the tree line in the Himalayas and other mountain ranges is gradually moving upward, encroaching on the alpine zones where snow leopards live. This encroachment reduces the available habitat for snow leopards and can lead to increased competition with other predators and conflicts with human activities
Adapting to Rapid Environmental Shifts
Snow leopards have shown remarkable adaptability to environmental changes, but the rapid pace of climate change may outstrip their ability to adapt. For instance, changes in temperature and precipitation patterns can affect the availability and distribution of prey species, forcing snow leopards to adjust their hunting strategies and diet
A study published in Global Change Biology highlighted that snow leopards are increasingly preying on livestock due to the decline in wild prey populations caused by habitat degradation and climate change. This shift not only affects the snow leopards’ diet but also heightens the risk of human-wildlife conflict, which can lead to retaliatory killings
Conservation Efforts in Changing Climates
Conservation organizations are actively working to mitigate the impacts of climate change on snow leopards
Strategies include habitat restoration, creating wildlife corridors to ensure connectivity between fragmented habitats, and implementing community-based conservation programs that involve local people in protecting snow leopards
Efforts to combat climate change, such as reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting sustainable land use practices, are also essential for preserving snow leopard habitats
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) and other organizations emphasize the need for a comprehensive approach that addresses both the immediate and long-term threats posed by climate change
Conclusion
Snow leopards exhibit remarkable adaptations that enable them to survive in diverse and often harsh climatic conditions. Their thick fur, large paws, and muscular build are physical traits that help them navigate and thrive in cold, mountainous regions
Behaviorally, they adapt their hunting techniques, sheltering habits, and energy conservation strategies to suit the environments they inhabit. Their diet varies with prey availability, and genetic adaptations have equipped them to cope with high altitudes and cold climates. However, climate change presents significant challenges, altering habitats and prey availability at a pace that may exceed their ability to adapt
Effective conservation strategies that address these challenges are crucial for ensuring the survival of these majestic creatures in a rapidly changing world. By understanding and supporting these adaptive traits and implementing comprehensive conservation efforts, we can help secure a future for snow leopards across their range